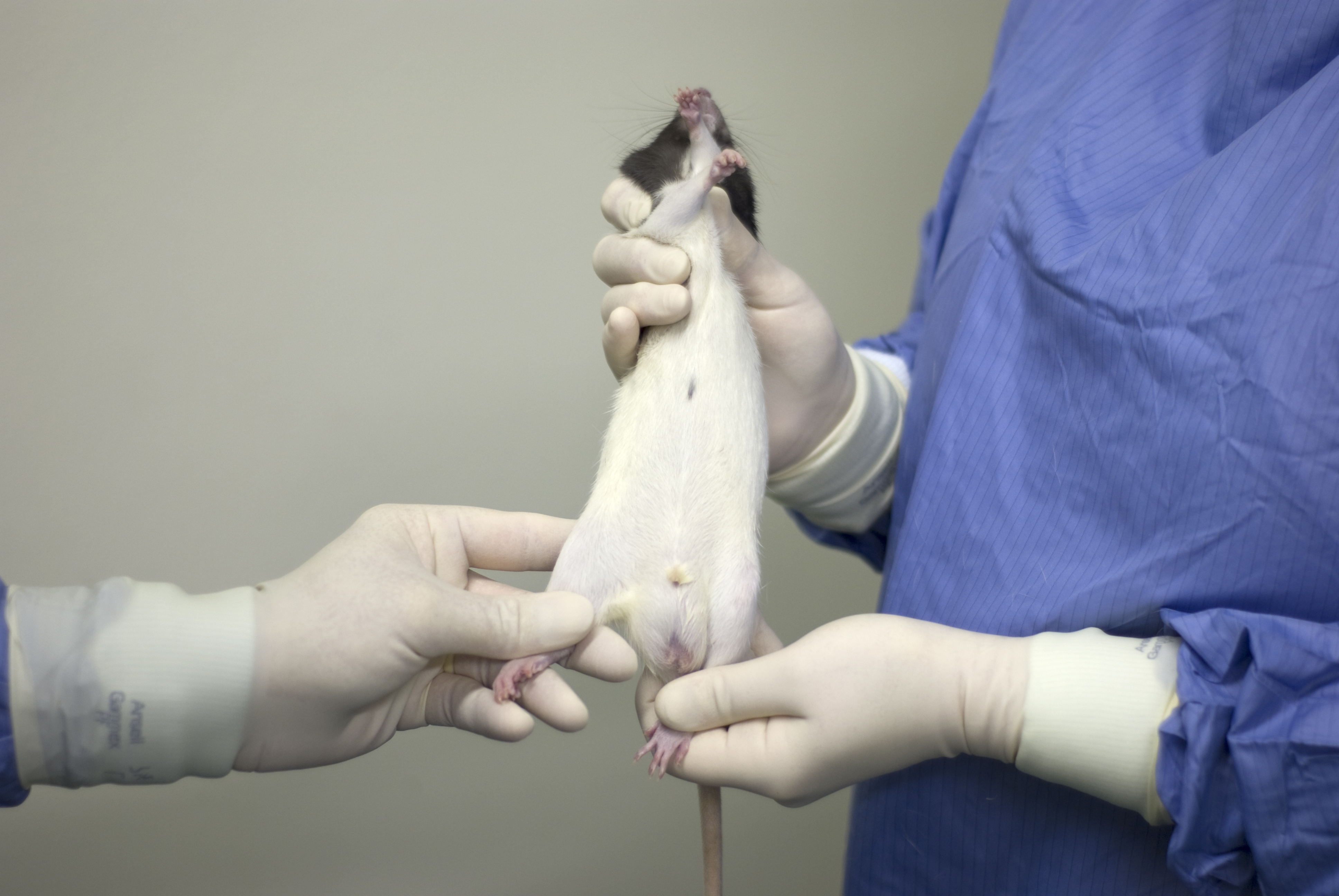
Intraperitoneal injection of a substance in the rat
Key points to note
Although widely used as a means of administering substances, particularly injectable anaesthetics, this is an inherently unreliable technique, since inadvertent injection of some material into the gut, abdominal fat and subcutaneous tissues is a relatively frequent occurrence (Steward et al, 19681, Gaines Das and North, 20072). For this reason, it may be preferable to use other routes such as subcutaneous or oral administration.
It is not usually necessary to try to sterilise the skin with antiseptics – their use is almost always ineffective and they simply prolong the duration of restraint needed and may cause additional disturbance to the animal.
As with all injection sites, using a new needle for each animal, and injecting fluid that is at body temperature will reduce any discomfort caused by the procedure.
Material that is irritant or with a high or low pH can cause pain both during and following injection.
As with other routes, if repeated injections of material are needed, consider alternatives such as the use of minipumps.